Operational Audit Services
Operational auditing is a methodical technique for assessing the efficacy and efficiency of an organization’s operations. After Operational Auditing is complete, the management will receive a report with the findings of the assessment and suggestions for enhancements. This indicates that the internal auditor extends his or her scope beyond financial controls to include operational areas that are intended to improve the Organization’s operations and internal control framework for day-to-day operations. An operational audit will assist in locating areas of non-conformity in the application of procedures. The management will be aided in taking corrective action.
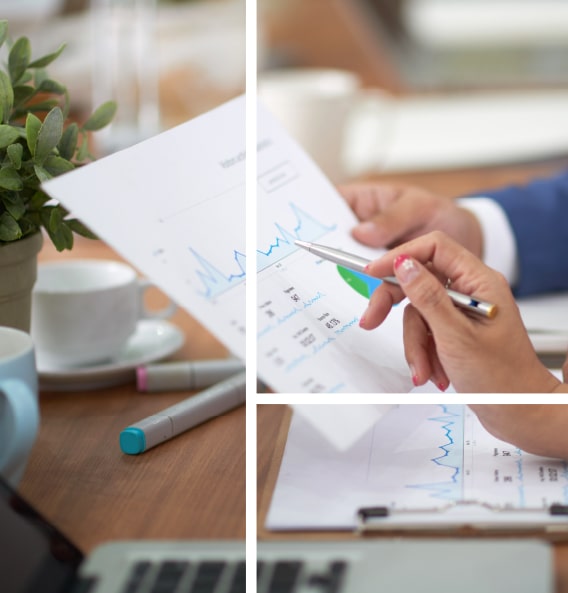

BRINGING CLARITY FROM COMPLEXITY
Global Strategic Partners Union
services for a global network of creators
We gives you unmatched agility without compromising on experience
1

Branding & identity
It has survived not only five centu ipsum duos.

Data engineering
It has survived not only five centu ipsum duos.
2
Project planning
It has survived not only five centu ipsum duos.
3

HR support
It has survived not only five centu ipsum duos.
4
Operational auditing’s goals
The following are some of the goals of operational auditing:
- Review the company’s policies, practices, and action plans.
- Attain increased profitability.
- Ascertain the effectiveness of the current procedures by putting control measures in place.
- Measurement of performance based on labour productivity.
- Promote socially responsible business practices.
Role and Responsibilities
The CEO and/or General Manager are primarily in charge of overseeing the day-to-day business activities. However, the Process Owner or Line Manager in charge of that operation or process will be accountable for each specific function or process covered by the Operational Audit.
Procedures for Operational Audit
- Knowing the company’s operational hierarchy and organizational structure.
- Having a thorough understanding of the current Policies, Procedures, and manuals for each function or process.
- Application of the currently established defined policies and procedures is walked through or field checked.
- Examining the holes or weaknesses in the current procedures.
- Recommendations to the management for closing the loopholes and establishing internal controls (if none already exist).
- To ensure that activities proceed without interruption by using the provided solutions and advice.
- To carry out a follow-up audit to evaluate the operation’s operational effectiveness.
Operational auditing tasks
- The degree to which senior management has succeeded in ensuring that all organisational operations are focused on boosting profits.
- Methods for reducing waste or loss by revealing the gaps or potential trouble spots between different levels of staff as well as between line management and the senior level.
- Deviations from the established goals and policies.
- To overcome undesirable outcomes and conditions, corrective action is required.
- Evaluation of one’s performance.
- Cost-cutting initiative.
- Physical operations issues.
- Examine the operating departments’ goals, including how production is carried out and how results are evaluated.
- Examine scrap, salvage, regular, and unusual wastages.
- Planning and managing the production process.
Discussion and Reporting
For busy executives to read, understand, and act on the findings of our work, the reporting should be straightforward and concise. The operational audit report details the findings, auditor recommendations for the reported findings, management measures to be performed, process owner responsibilities, and the goal date for the observation’s closure.
This report needs to be thoroughly addressed with management and the process owner to assist managers in assessing and analyzing how the business is now run and locating potential areas for improvement.
There is no legal requirement for a business to perform an operational audit. When management wants to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of the company’s operations, an operational audit is carried out. It aids Management in enhancing the financial processes’ ability to save money where operations are based on financial statements.
SCALE NEW HEIGHTS OF SUCCESS WITH US
Expert business partner to ensure business success!!!
A reliable partner with a team of experts delivering advice on business challenges to ensure long-term success and credibility in 500+ Global Conglomerates across diversified sectors.
Bringing Clarity from Complexity
GSPU ADVISORY!
Simplifying complex structures reviewing the vital elements, and spotting effective tools for communication to assist clients make informed decisions and drive progress.
COMPATIBLE
CUSTOMISABLE

CONVENIENT






